I’ll start with a description of what Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning are I stole from Medium1 and Nvidia2.
Artificial Intelligence
First coined in 1956 by John McCarthy, AI involves machines that can perform tasks that are characteristic of human intelligence. While this is rather general, it includes things like planning, understanding language, recognizing objects and sounds, learning, and problem solving.
We can put AI in two categories, general and narrow. General AI would have all of the characteristics of human intelligence, including the capacities mentioned above. Narrow AI exhibits some facet(s) of human intelligence, and can do that facet extremely well, but is lacking in other areas. A machine that’s great at recognizing images, but nothing else, would be an example of narrow AI.
Machine Learning
A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some task T and some performance measure P, if its performance on T, as measured by P, improves with experience E.
At its core, machine learning is simply a way of achieving AI. Arthur Samuel coined the phrase not too long after AI, in 1959, defining it as, “the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed.” You see, you can get AI without using machine learning, but this would require building millions of lines of codes with complex rules and decision-trees.
To give an example, machine learning has been used to make drastic improvements to computer vision (the ability of a machine to recognize an object in an image or video). You gather hundreds of thousands or even millions of pictures and then have humans tag them. For example, the humans might tag pictures that have a cat in them versus those that do not. Then, the algorithm tries to build a model that can accurately tag a picture as containing a cat or not as well as a human. Once the accuracy level is high enough, the machine has now “learned” what a cat looks like.
Types of machine learning:
- Supervised: We choose a model class: y=f(x;W)- a model class f is a way of using some numerical parameters W, to map each input vector x into a predicted output y
- Regression problem (return a continuous real value)
- Classification problems(return a discrete value)
- Unsupervised learning - some benefits: it provides a low dimensional representation of the input; economical high representation of the input in terms of learned features; it finds sensible clusters in the input
- Clustering problem (given unlabeled data group similar stuff together)
- Cocktail Party problem (find structure in a chaotic environment)
- Reinforcement learning - Learn to select an action to maximize payoff
- Recommended systems
Deep Learning
Deep learning is one of many approaches to machine learning. Other approaches include decision tree learning, inductive logic programming, clustering, reinforcement learning, and Bayesian networks, among others. Deep learning was inspired by the structure and function of the brain, namely the interconnecting of many neurons. Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are algorithms that mimic the biological structure of the brain.
Unlike a biological brain where any neuron can connect to any other neuron within a certain physical distance, these artificial neural networks have discrete layers, connections, and directions of data propagation.
Each neuron assigns a weighting to its input — how correct or incorrect it is relative to the task being performed. The final output is then determined by the total of those weightings. So think of our stop sign example. Attributes of a stop sign image are chopped up and “examined” by the neurons — its octogonal shape, its fire-engine red color, its distinctive letters, its traffic-sign size, and its motion or lack thereof. The neural network’s task is to conclude whether this is a stop sign or not. It comes up with a “probability vector,” really a highly educated guess, based on the weighting. In our example the system might be 86% confident the image is a stop sign, 7% confident it’s a speed limit sign, and 5% it’s a kite stuck in a tree ,and so on — and the network architecture then tells the neural network whether it is right or not.
Why has deep learning taken off recently?
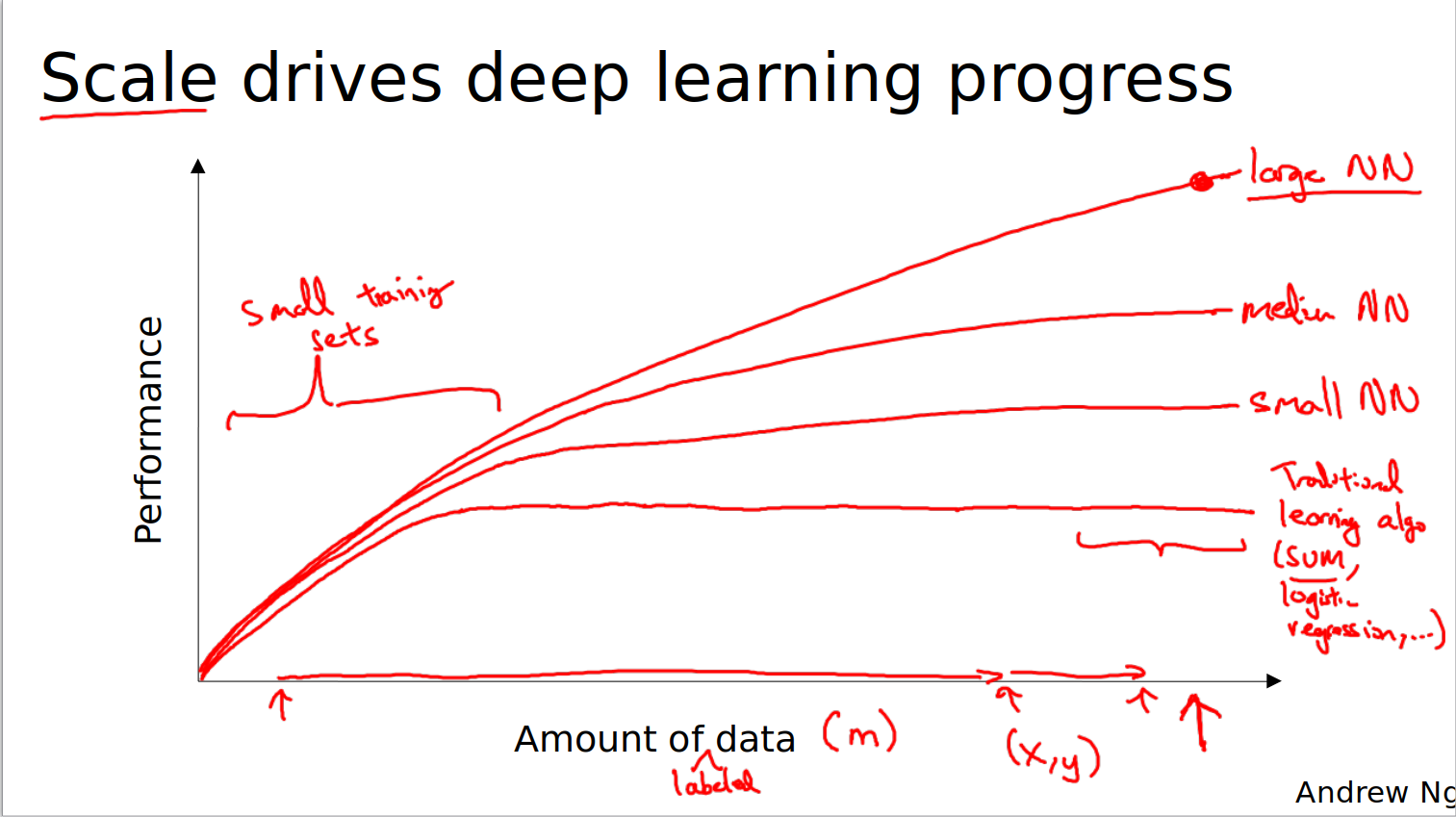
In recent years more and more data has become available online. One of the best ways to increase the performance of a deep learning model is to make it more complex and give it a larger dataset.
The combination of this two factors has led to the popularization of deep learning.
We also have more and more computing power at our disposal, making the training of larger and larger models feasible. Improvements have also been made to the algorithms themselves, for instance switching from using the sigmoid activation function to using ReLU activation function. In the case of the sigmoid, at the tails of the function the gradients tend to vanish, whereas with ReLU this does not happen; this means that using ReLU activation a network converges faster during training.
Resources
- Articles:Artificial_Intelligence_Articles